Macroscopic (MACRO) Examination
CTOD is a test method for the determination of a metal’s resistance to the initiation of a crack resulting from notch defects. CTOD measures the elastic-plastic toughness of the metal in the ductile-brittle transition.
The propagation of a crack in a welded structure depends upon various factors including the material used, the size and sharpness of any notch present, operating temperature, the degree of restraint and welding procedure requirements.
involves cyclic loading.
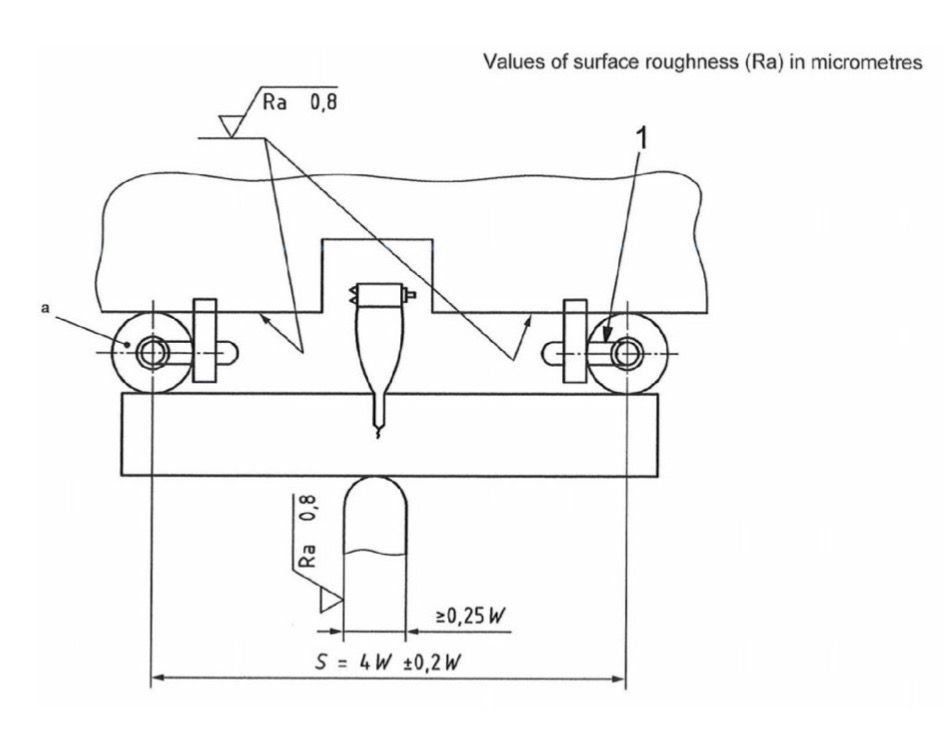
The CTOD test permits full size specimens to be used irrespective of metal thickness, to which a notch of given width and depth is applied. The specimen in then subject to a high speed resonance load cycling to induce a crack at the root of the notch. The specimen is then cooled to test temperature and force is applied to open the notch using a three point bending rig. A clip gauge fixed to the mouth of the notch accurately measures the slow opening of the crack and a force sensing device enables the applied load to be plotted against displacement on a graph. The material beneath the crack will either deform plastically or fracture without loss in section.